Components of Computer and their Functions
We offer you a brighter future with FREE online courses - Start Now!!
A computer system is not a single device or setup that functions on its own. It is made of several components which have specific functions and features to support the entire system. While there are many devices under one system, they are divided into three basic components of the computer system. They make data processing and performing tasks easier and convenient.
The main three components are – Input Unit, Output Unit, and Central Processing Unit. The central processing unit is further divided into memory or storage unit, control unit, and arithmetical and logical unit. Each unit has its own special feature to assist the system.
The input unit is mandatory for taking in the instructions, the processing unit is important for understanding them and the output unit enables the delivery of results. They all rely on each other at every step and together accomplish all the tasks.
One thing to keep in mind is that the external appearance of these units might differ from system to system. But at the end of the day, they will perform the same set of tasks as others. Let us take a look at each of the components in detail with their distinctive functions.
https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/cdn-uploads/Components-of-a-digital-computer.jpg
1. Input Unit of Computer System
The computer system responds to the instruction it receives from the users. And to get those instructions, a computer needs an input unit. This includes all the input devices responsible for reading the data entered by the user.
The system doesn’t respond unless it receives a command from the user using the input unit or the input devices. The users use numbers, letters, images, etc. to enter the command, the input devices are the ones accepting them. For example – we use a keyboard to enter a text, the keyboard here becomes the input unit.
Functions of Input Unit of a Computer System
- Takes in user commands in the form of data.
- Converts data in a digital language format.
- Sends over the data to the processing unit for the next step.
Examples of Input Unit
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- JoyStick
- Light pen
- Track Ball
- Scanner
- Graphic Tablet
2. Output Unit of Computer System
The user, when sending a set of instructions to the computer, reaches the output device in the end. The execution of command takes place here and the users get their results.
The processor sends the transcripted instructions to the output devices for execution. These devices always have a connection to the system and thus the coordination is quite easy.
The monitor is one of the main output devices which displays the results to the user. Everything that the input devices receive, reaches the output devices eventually. All the execution activities take place inside the mechanism of a device.
Functions of Output Unit of Computer
- Receives the instructions in machine language to execute a task.
- Coordinates with the processor to get the instruction on time.
- Converts the machine language back into a user-friendly one by completing tasks.
- It is the medium by which users understand that their demands are met by the system.
Examples of Output Unit of a Computer
- Monitor – variants
- Printers – all types
- Plotters
- Projector
- LCD Projection Panels
- Computer Output Microfilm
- Speaker
- Headphones
- Ear Plugs
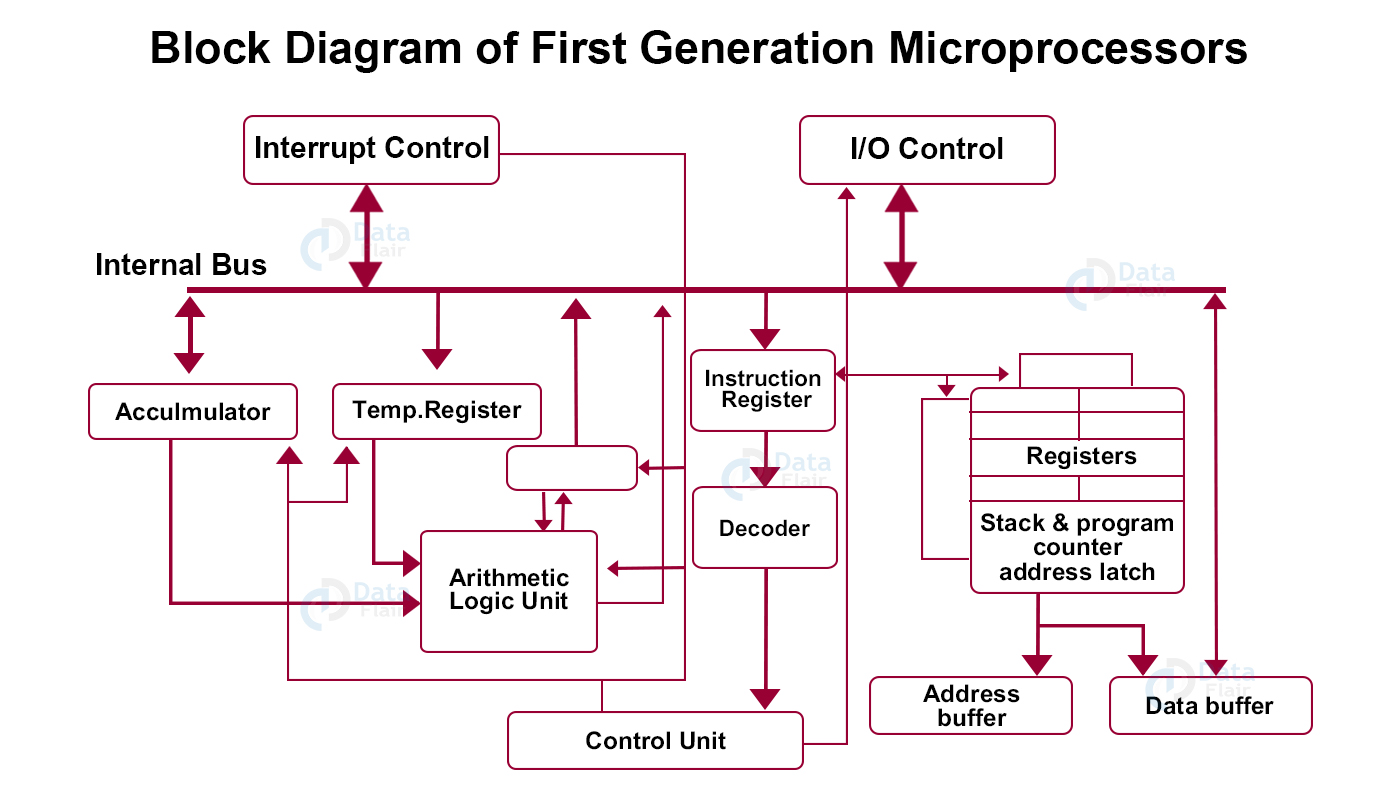
3. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
The data that the input unit accepts goes to the processing unit before execution. This unit understands what the command actually is and how they can achieve it. It converts data accepted in human language into machine language for computers to understand. It has a mainboard with a central chip which is the primary part of the processor.
The processor coordinates with both input and output devices to make things done. It has three main components –
a. Memory Unit
This component of the CPU deals with strong data. When the data reaches the processor from the input devices, the memory unit saves it immediately. It has some pre-existing programs which help in transmitting the data to the other parts of the CPU. Similarly, the completion of a task by output device is also saved here before it reaches the user. The processor cannot process the data unless the memory unit saves it.
This is where all the information becomes accessible for the user. It uses bits and bytes to measure data size. The memory unit further divides into primary and secondary storage units.
The primary memory is internal and temporary. RAM is the primary memory in this case. It stores the commands for a short time and is volatile in nature.
The secondary storage is non-volatile and permanent. But not directly accessible. The data needs to transfer to the primary unit and then the processor can access it.
Functions of Memory Unit In Computer
- Responsible for storing data coming from input devices.
- Storing the result data coming from output devices.
- Storing all the steps that the system goes through while task execution.
b. Control Unit
This unit is to manage the computer device functioning and is the central component of the processor unit. Once the data is in the memory, it processes it for further execution. It is where the data conversion from human language to machine language takes place. It interprets the signal and sends it over to the output unit. Once the result is out, it retrieves the data again and presents it to the user.
Functions of Control Unit in Computer
- Coordinate information transfer between the memory and I/O devices.
- Converts the instruction into machine language.
- It decodes the instruction and sends it to the correct device.
- Prepare a data sequence making it easier for processing.
- Maintains a flow of data inside the system.
- Transfer the commands/issues to the arithmetic and logic unit.
c. Arithmetic & Logical Unit (ALU)
This unit of processor takes care of mathematical calculations and issues that the computer system faces while functioning. It is also useful for data comparison and actions including decision making. It has features to facilitate different mathematical solutions like addition, subtraction, multiplication, etc.
ALU gets the data from the memory in the form of registers. These registers are for a memory address, data manipulation, and processing. They may have distinctive features sometimes. The ALU performs the calculation only when needed and then sends it to the output devices.
Functions of ALU in Computer
- Responsible for all calculations and mathematical issues.
- Allows the computer to compare data easily.
- Enables the data transfer between primary and secondary memory by decoding it.
- Acts as a decision-maker in case of any trouble.
Conclusion
A computer system has many building blocks that help in its functioning. They are quite important to understand since we use them every day. Having enough and correct knowledge about them can save us from wasting time and maintaining device security. They are also important from the exam point of view.
Many competitive exams, as well as college exams, ask this topic in the general knowledge section. And many might have it under the computer awareness section. Thus reading the details carefully can lead to fruitful exam results.
If you are Happy with DataFlair, do not forget to make us happy with your positive feedback on Google


I’m satisfied
my mostly doubts got cleared
Good job but reference should always be included at the end of the work
very nice and clear explanation.
great work,congrats
This helped
For me it is a good and awesome transitional tanscripts.
Good answers
Nice