Co-Cultures: Growing together gives more rice and aquatic food
When you eat rice with fish – or rice with crab or shrimp – you probably do not think about where the food came from. And if you do, you probably think that the rice grew in a paddy field, while the fish, crab or shrimp were caught in the sea. However, this may only be partially true. Systems for growing rice and various aquatic animals together have existed for over 1,200 years, but the practice of ‘co-culture’ has only recently gained the attention of the major rice-producing nations and the scientific community (Xie et al., 2011).
Rice is one of the most widely consumed grains in the world and is grown in more than 100 countries. It is a staple food source for over half of the world’s population and of upmost importance for lower income countries in Asia, Latin America and Africa (Bashir et al., 2020). Climate change, declining natural resources and an ever-growing population put immense pressure on both increasing yields and reducing the environmental footprint of rice (Hu et al., 2016; Ahmed and Turchini, 2021). Global trends are thus moving towards sustainable and organic management of biological resources (Chen et al., 2014; Muller et al., 2017). Strategic coupling of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, such as growing crops and aquatic animals together, could help meet this target (Ahmed and Turchini, 2021).
Previous research has shown that co-cultures can boost yields, improve soil health and enhance ecosystem services (Mueller et al., 2012; Campanhola and Pandey, 2019). But even though co-culture systems would help optimise the use of land and water resources to produce food – while reducing the environmental impacts associated with rice monocultures – large-scale and long-term data are lacking (Bashir et al., 2020).
Now, in eLife, Xin Chen and colleagues at Zhejiang University and Bioversity International – including Liang Guo and Lufeng Zhao as joint first authors – report new evidence in support of co-cultures with aquatic animals and rice crops (Guo et al., 2022). Between 2017 and 2020, the team conducted three separate field experiments in which rice was grown with either fish, crabs or soft-shelled turtles. Each set-up also included a control experiment, where rice was grown as a monoculture. No agrochemicals were used to control weeds, pests or diseases during the field trials.
Over the four years, the co-cultures demonstrated multiple benefits (Figure 1). Rice yield was consistently higher in fields containing aquatic animals (between 8.7% and 12.1%). Moreover, the team was also able to harvest significant amounts of fish, crab and turtle as food (between 560 and 2660 kg/ha). Co-cultures also had fewer weeds and maintained consistent levels of mineral nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus) in the soil. Moreover, the breakdown of organic matter happened faster in the co-cultures.
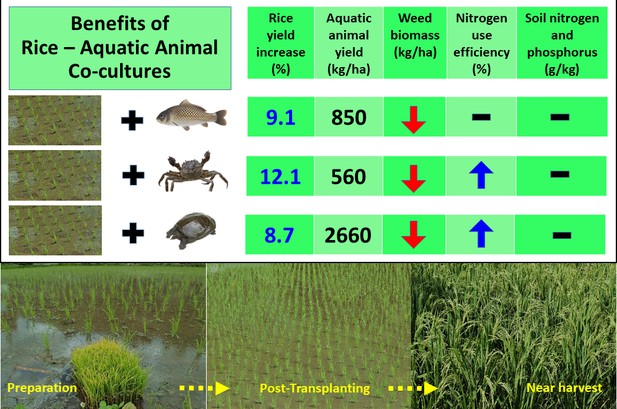
The benefits of co-culture for growing rice.
Guo et al. showed that growing rice with aquatic animals (fish, crabs or turtles) increases rice yield, suppresses the growth of weeds, and maintains the levels of nitrogen and phosphorus in the soil. Growing rice with crabs or turtles was also shown to promote a more efficient use of nitrogen. The photographs show the field before (left) and after (middle) the rice plants were transplanted, and near harvest time (right). The aquatic animals were introduced as juveniles about a week after transplanting and lived with the rice plants throughout the experimental periods.
Animals are instrumental in moving elements, such as carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus, in the environment (Schmitz et al., 2018). To find out whether the biology of a co-cultured animal would affect the growth of rice, Guo et al. carried out three additional, controlled experiments to trace the movement of nitrogen from feed (labelled with stable isotopes) to aquatic animals and the environment.
Analyses of the animal’s food intake revealed that fish and crabs obtained up to half of their diet (50% and 35%, respectively) from the rice fields, consuming algae, phytoplankton or weeds. Turtles relied more on additional feed, and only derived 16% of their food intake naturally. The animals’ wastes and any uneaten feed also increased the nutrient availability for the rice plants: rice plants used up to a third of the nitrogen from the animal feed.
The work of Guo et al. demonstrates clearly how co-cultures could make agriculture more sustainable, by increasing soil fertility and reducing the need for fertilizers or pesticides. Moreover, these coupled systems could also help fight the spread of malaria by introducing natural, co-culturing predators, such as frogs (which eat the mosquitos) and fish (which eat the mosquito larvae), and so contribute towards several ‘Sustainable Development Goals’ of the United Nations (Khatiwada et al., 2016; Campanhola and Pandey, 2019).
More research is needed to better understand the impact of co-culture on greenhouse gas emissions and nutrient pollution (Bashir et al., 2020). Nevertheless, these experiments provide a good foundation for further studies to explore how agriculture can be made more sustainable.
References
-
The evolution of the blue-green revolution of rice-fish cultivation for sustainable food productionSustainability Science 16:1375–1390.https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-021-00924-z
-
Co-culture of rice and aquatic animals: An integrated system to achieve production and environmental sustainabilityJournal of Cleaner Production 249:119310.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119310
-
Can the co-cultivation of rice and fish help sustain rice production?Scientific Reports 6:28728.https://doi.org/10.1038/srep28728
-
Frogs as potential biological control agents in the rice fields of Chitwan, NepalAgriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 230:307–314.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2016.06.025
-
Animals and the zoogeochemistry of the carbon cycleScience (New York, N.Y.) 362:eaar3213.https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar3213
Article and author information
Author details
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank SLU Aquaculture and Jordbruksverket for financial support.
Publication history
- Version of Record published: February 22, 2022 (version 1)
Copyright
© 2022, Liu et al.
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use and redistribution provided that the original author and source are credited.
Metrics
-
- 1,149
- views
-
- 127
- downloads
-
- 2
- citations
Views, downloads and citations are aggregated across all versions of this paper published by eLife.
Download links
Downloads (link to download the article as PDF)
Open citations (links to open the citations from this article in various online reference manager services)
Cite this article (links to download the citations from this article in formats compatible with various reference manager tools)
Further reading
-
- Ecology
- Evolutionary Biology
Seasonal animal dormancy is widely interpreted as a physiological response for surviving energetic challenges during the harshest times of the year (the physiological constraint hypothesis). However, there are other mutually non-exclusive hypotheses to explain the timing of animal dormancy, that is, entry into and emergence from hibernation (i.e. dormancy phenology). Survival advantages of dormancy that have been proposed are reduced risks of predation and competition (the ‘life-history’ hypothesis), but comparative tests across animal species are few. Using the phylogenetic comparative method applied to more than 20 hibernating mammalian species, we found support for both hypotheses as explanations for the phenology of dormancy. In accordance with the life-history hypotheses, sex differences in hibernation emergence and immergence were favored by the sex difference in reproductive effort. In addition, physiological constraint may influence the trade-off between survival and reproduction such that low temperatures and precipitation, as well as smaller body mass, influence sex differences in phenology. We also compiled initial evidence that ectotherm dormancy may be (1) less temperature dependent than previously thought and (2) associated with trade-offs consistent with the life-history hypothesis. Thus, dormancy during non-life-threatening periods that are unfavorable for reproduction may be more widespread than previously thought.
-
- Ecology
Declines in biodiversity generated by anthropogenic stressors at both species and population levels can alter emergent processes instrumental to ecosystem function and resilience. As such, understanding the role of biodiversity in ecosystem function and its response to climate perturbation is increasingly important, especially in tropical systems where responses to changes in biodiversity are less predictable and more challenging to assess experimentally. Using large-scale transplant experiments conducted at five neotropical sites, we documented the impacts of changes in intraspecific and interspecific plant richness in the genus Piper on insect herbivory, insect richness, and ecosystem resilience to perturbations in water availability. We found that reductions of both intraspecific and interspecific Piper diversity had measurable and site-specific effects on herbivory, herbivorous insect richness, and plant mortality. The responses of these ecosystem-relevant processes to reduced intraspecific Piper richness were often similar in magnitude to the effects of reduced interspecific richness. Increased water availability reduced herbivory by 4.2% overall, and the response of herbivorous insect richness and herbivory to water availability were altered by both intra- and interspecific richness in a site-dependent manner. Our results underscore the role of intraspecific and interspecific richness as foundations of ecosystem function and the importance of community and location-specific contingencies in controlling function in complex tropical systems.






