Religion is a set of social-cultural systems characterized by beliefs, practices, morals, behaviors, texts, and prophecies.
What Is Religion?
Although there is no specific definition of religion, it is mainly a belief system involving worship of a supernatural or spiritual entity/entities, such as Gods and Goddesses. It may involve a number of practices and activities like praying, chanting hymns, worshipping a shrine, temple or church and other rituals. It can be considered as an organized community-based practice based on beliefs and behaviors and can involve certain religious practices, mythology, or rituals.
“Religion is often related to the idea of the ‘transcendent’ with certain beliefs, practices and behavioral rules associated with it; it is organized and often community-based, but can also be practiced privately,” says a 2015 study 1 Koenig H. G. (2015). Religion, spirituality, and health: a review and update. Advances in mind-body medicine, 29(3), 19–26. . Most people follow the religion they are born to. While others are seen to convert to a religion of their choosing or after they get married. Some people may even choose to not follow any religion. In this case, they are known as atheists.
Religious beliefs include practices or rituals such as prayer, meditation, and engagement with their respective community members. For followers, God is perceived as a form of support and strength to deal with life challenges. A 2007 study 2 Park C. L. (2007). Religiousness/spirituality and health: a meaning systems perspective. Journal of behavioral medicine, 30(4), 319–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-007-9111-x pointed out that religion, spirituality, or belief has been seen as the lenses through which some people interpret, understand, evaluate and respond to their experiences in the world and give people a sense of meaning and purpose of life.
Types Of Religion
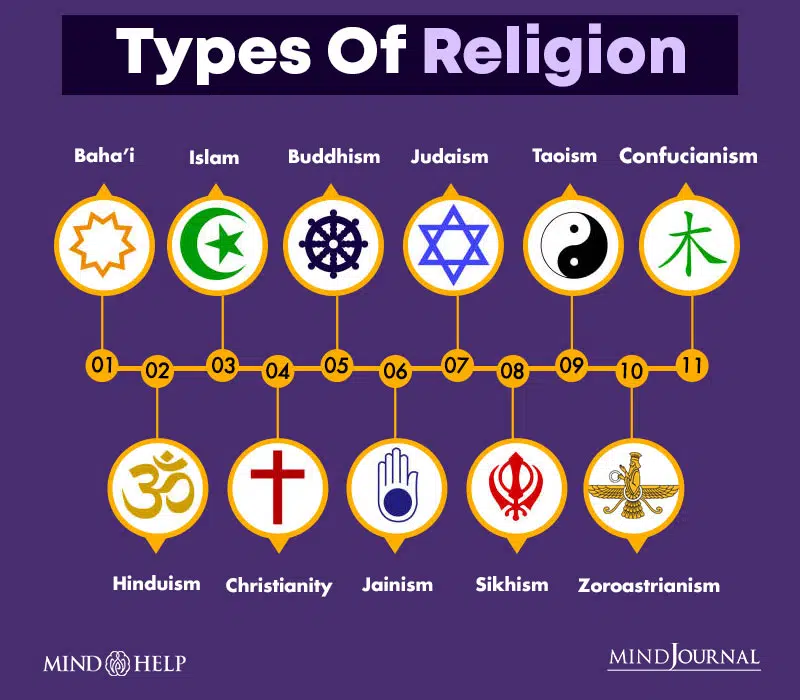
There are several religions followed by populations across the world. Some people believe in following one god or monotheism, while others believe in many gods or polytheism. Some of the major types of religions can include:
- Baha’i
- Hinduism
- Islam
- Christianity
- Buddhism
- Jainism
- Judaism
- Sikhism
- Taoism
- Zoroastrianism
- Confucianism
A 2013 study 3 Rote, S., Hill, T. D., & Ellison, C. G. (2013). Religious attendance and loneliness in later life. The Gerontologist, 53(1), 39–50. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/gns063 found that religion, spirituality, or belief are important for many people in providing structure, meaning, and understanding to everyday life and also support through life challenges. A 2015 study 4 Agli, O., Bailly, N., & Ferrand, C. (2015). Spirituality and religion in older adults with dementia: a systematic review. International psychogeriatrics, 27(5), 715–725. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1041610214001665 indicated that the potential benefits of religion, spirituality, and belief improved the health, well-being, and quality of life, particularly in older adults.
Understanding Religion
Religion and beliefs play a significant role in influencing one’s identity and the way one perceives the world around them. Certain religions also have certain rituals, norms, and disciplines that may also shape a person’s likes, dislikes, and characteristics. It is also considered to be an approach with which people deal with life concerns and challenges. This phenomenon is often expressed by following different rituals and practices.
It displays one’s relationship with God. Believers often engage in devotional practices such as prayers, songs, reading scriptures, or meditation. Some religions have sacred histories that are preserved in scriptures and writings. These scriptures are followed by the community members. For instance, the Bible is followed by the Christians. Religion exists in every culture and almost 85% 5 Koenig H. G. (2012). Religion, spirituality, and health: the research and clinical implications. ISRN psychiatry, 2012, 278730. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/278730 of the world population follow some form of religious belief.
It is followed to understand the meaning, purpose, and origin of life. It may contain symbolic stories that followers consider sacred and holy. Although religion is a common practice, some psychologists believe that religious beliefs are a social force that encourages irrational thoughts and behaviors. Religious differences are often found to have a significant impact on society at large. For instance, in Christianity, the rift between Protestants and Catholics is still prevalent. A recent report found that people of a faith other than catholic will not be formally invited to Eucharist, the sharing of bread and wine.
Research suggests that religion is a result of how our brain perceives the world, our cognitive tendencies to organize and anthropomorphize our surroundings, and our beliefs about the world. Several studies 6 Puchalski C. M. (2001). The role of spirituality in health care. Proceedings (Baylor University. Medical Center), 14(4), 352–357. https://doi.org/10.1080/08998280.2001.11927788 have shown that many patients use religion to cope with medical and non-medical problems. Positive religious coping has shown a lot of benefits. It usually involves seeking a lesson from God for a stressful event, having faith, seeking support, and supporting others. Religious practices can help to maintain mental health and prevent psychiatric conditions. It can help to cope with anxiety, fears, frustrations, anger, feelings of inferiority, and isolation.
One of the most commonly used practices is meditation. There are several benefits of practicing meditation. They include changes in personality, reduced tension and anxiety, stabilized emotional dysregulation, and improved self-knowledge. Reports 7 Hoge, E. A., Bui, E., Marques, L., Metcalf, C. A., Morris, L. K., Robinaugh, D. J., Worthington, J. J., Pollack, M. H., & Simon, N. M. (2013). Randomized controlled trial of mindfulness meditation for generalized anxiety disorder: effects on anxiety and stress reactivity. The Journal of clinical psychiatry, 74(8), 786–792. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.12m08083 have also found that meditation can improve panic attacks, generalized anxiety disorder, depression, insomnia, drug use, stress, chronic pain, and others. Hence, building a better relationship with God and finding spiritual direction can mentally and physically benefit a person.
Read More About Generalized Anxiety Disorder Here
Religion And Spirituality
It should be noted that religiosity and spirituality may be separate from each other. While religion is a system of beliefs, practices and rituals that helps us connect with a higher power, the supreme being or the ultimate truth, spirituality is a personal drive to understand the self, the soul, life and our relationship with a higher power. It may or may not involve religious practices or a community. However, both are interrelated 8 Vitorino, L. M., Lucchetti, G., Leão, F. C., Vallada, H., & Peres, M. (2018). The association between spirituality and religiousness and mental health. Scientific reports, 8(1), 17233. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35380-w as higher levels of religiousness and spirituality are associated with better outcomes. Being both religious and spiritual can help us “in coping, survival and maintaining overall wellbeing,” according to research.
Aspects Of Religion
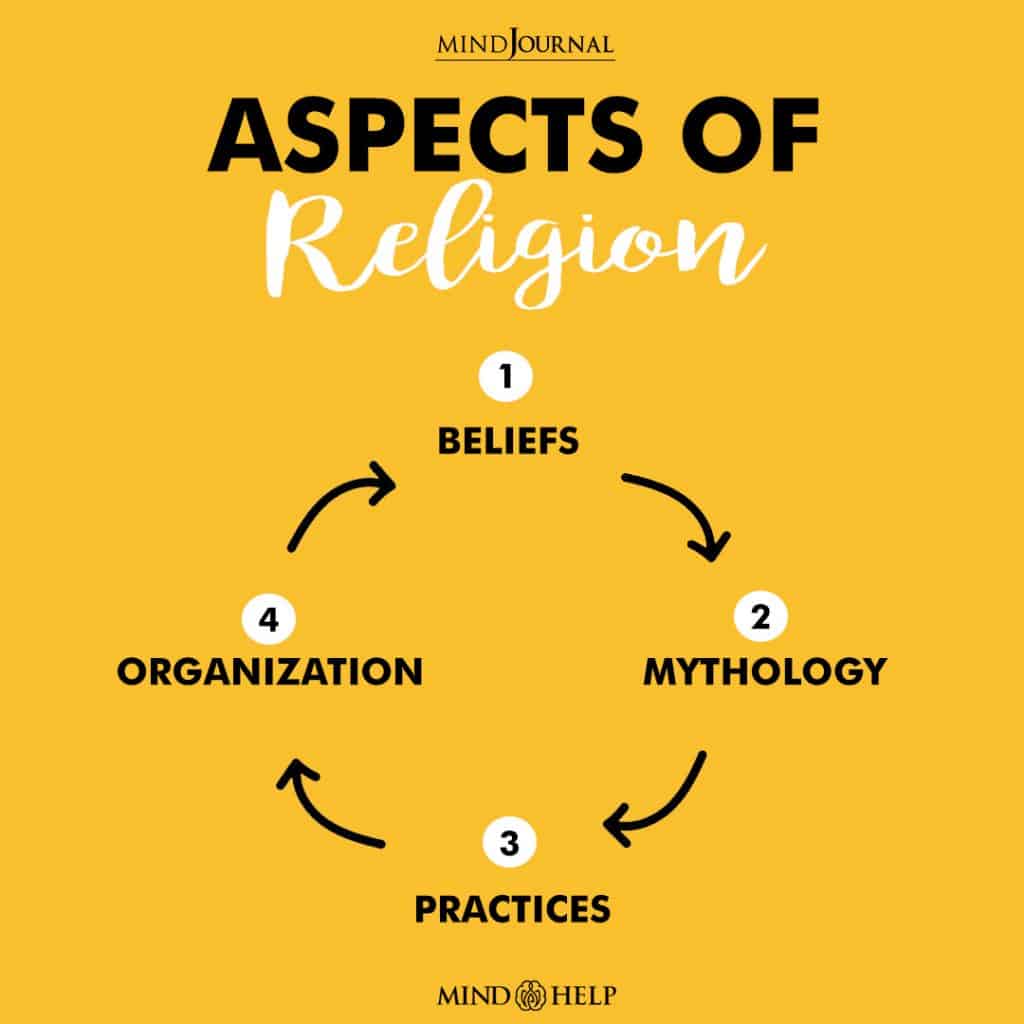
It is a source of guidance and comfort. It is built out of beliefs, sacred texts, mythology, practices and other forms. Some of the aspects can include:
1. Beliefs
Belief can be defined as an attitude or state of mind despite being unable to prove it. Faith and belief are an essential part of this phenomenon. Although belief is a state of mind, religious beliefs are an organized set of beliefs dictated by a particular religion.
2. Mythology
Mythology can be defined as narratives that play a significant role in society. The main characters in mythology are usually gods, demigods, deities or supernatural figures. Religion and mythology are closely interrelated. Some of the ancient polytheistic religions that are categorized under mythology are Greece, Rome, and Scandinavia. These mythologies have played a key role in the development of religion.
3. Practices
Religion is constituted of several practices such as rituals, ceremonies, sacrifices, festivals, feasts, prayer, music, dance, community service, meditation, and others. A 2001 study 9 Quinn, M. T., Cook, S., Nash, K., & Chin, M. H. (2001). Addressing religion and spirituality in African Americans with diabetes. The Diabetes educator, 27(5), 643–655. https://doi.org/10.1177/014572170102700505 found that spiritual and religious belief and practicing it can aid in coping with a chronic illness by providing support, confidence, and hope.
4. Organization
Every religion has its own traditions that are practiced by its followers. This can constitute memberships, rules, and regulations.
Religion And Mental Health
Religion has been known to serve a greater purpose than humanity itself. It is found to have positively affected both mental and physical health. It can help to increase resilience while facing difficult situations. A 2019 study 10 Grim, B.J., Grim, M.E. Belief, Behavior, and Belonging: How Faith is Indispensable in Preventing and Recovering from Substance Abuse. J Relig Health 58, 1713–1750 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-019-00876-w found that religiousness can reduce suicide rates, alcoholism, and drug use. Religious beliefs influence how people deal with stress, suffering, and life challenges. It enhances acceptance and endurance. Religious beliefs generate peace, self-confidence, a sense of purpose, forgiveness, and a positive self-image. However, a 2006 study 11 Moreira-Almeida, A., Neto, F. L., & Koenig, H. G. (2006). Religiousness and mental health: a review. Revista brasileira de psiquiatria (Sao Paulo, Brazil : 1999), 28(3), 242–250. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1516-44462006000300018 indicated that it may also cause guilt, doubts, anxiety, and depression due to persistent self-criticism.
Religion also brings a sense of belonging among community members and initiates social connections. Humans are social creatures. Hence religion serves the purpose of creating and communicating with a community they belong to. A 2011 study 12 Umberson, D., & Montez, J. K. (2010). Social relationships and health: a flashpoint for health policy. Journal of health and social behavior, 51 Suppl(Suppl), S54–S66. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022146510383501 pointed out that belonging to a group can bring psychosocial development that can improve and promote health. This phenomenon is also found to help people who are grieving a loved one’s loss through ceremonies or groups organized by community members. For instance, grieving people can attend church groups that assist in coping with loss.
It is also an establishment that provides guidance and teachings about life. Every human being requires direction and guidance. Most people turn to religion in order to seek answers for life-altering situations or daily challenges. It is also known to inspire gratitude, compassion, and forgiveness among fellow community members or any other community members. It enhances an individual’s sense of being and awareness. An essential part of this phenomenon is to build a connection with God and your soul that contributes to one’s personal growth, spiritually and mentally. A 2013 study 13 Behere, P. B., Das, A., Yadav, R., & Behere, A. P. (2013). Religion and mental health. Indian journal of psychiatry, 55(Suppl 2), S187–S194. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5545.105526 (Retraction published Indian J Psychiatry. 2019 Jan;61(Suppl 3):S632) found that loving God was positively correlated with higher self-esteem.
A 2014 study 14 Brown, Q. L., Linton, S. L., Harrell, P. T., Mancha, B. E., Alexandre, P. K., Chen, K. F., & Eaton, W. W. (2014). The influence of religious attendance on smoking. Substance use & misuse, 49(11), 1392–1399. https://doi.org/10.3109/10826084.2014.912224 found that religiousness was related to decreased smoking and alcohol consumption. Another study pointed out that religious commitment and participation increased longevity, especially in men. Hence, this phenomenon can greatly impact one’s mental and physical well-being.
The Symbolism Of Religion
The importance of this phenomenon differs from one individual to another. It is an individual’s personal quest to find the answers to the deeper questions about life and understand its meaning. Religion is the guidance that everyone needs to fulfill their greater destiny.
Religion At A Glance
- Although there is no specific definition of religion, it is mainly a belief system involving worship of a supernatural or spiritual entity/entities, such as Gods and Goddesses.
- Religion and beliefs play a significant role in influencing one’s identity and the way one perceives the world around them.
- Religion is a source of guidance and comfort.
- It also brings a sense of belonging among community members and initiates social connections.
- Religion is the guidance that everyone needs to fulfill their greater destiny.
References:
- 1Koenig H. G. (2015). Religion, spirituality, and health: a review and update. Advances in mind-body medicine, 29(3), 19–26.
- 2Park C. L. (2007). Religiousness/spirituality and health: a meaning systems perspective. Journal of behavioral medicine, 30(4), 319–328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-007-9111-x
- 3Rote, S., Hill, T. D., & Ellison, C. G. (2013). Religious attendance and loneliness in later life. The Gerontologist, 53(1), 39–50. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/gns063
- 4Agli, O., Bailly, N., & Ferrand, C. (2015). Spirituality and religion in older adults with dementia: a systematic review. International psychogeriatrics, 27(5), 715–725. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1041610214001665
- 5Koenig H. G. (2012). Religion, spirituality, and health: the research and clinical implications. ISRN psychiatry, 2012, 278730. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/278730
- 6Puchalski C. M. (2001). The role of spirituality in health care. Proceedings (Baylor University. Medical Center), 14(4), 352–357. https://doi.org/10.1080/08998280.2001.11927788
- 7Hoge, E. A., Bui, E., Marques, L., Metcalf, C. A., Morris, L. K., Robinaugh, D. J., Worthington, J. J., Pollack, M. H., & Simon, N. M. (2013). Randomized controlled trial of mindfulness meditation for generalized anxiety disorder: effects on anxiety and stress reactivity. The Journal of clinical psychiatry, 74(8), 786–792. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.12m08083
- 8Vitorino, L. M., Lucchetti, G., Leão, F. C., Vallada, H., & Peres, M. (2018). The association between spirituality and religiousness and mental health. Scientific reports, 8(1), 17233. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35380-w
- 9Quinn, M. T., Cook, S., Nash, K., & Chin, M. H. (2001). Addressing religion and spirituality in African Americans with diabetes. The Diabetes educator, 27(5), 643–655. https://doi.org/10.1177/014572170102700505
- 10Grim, B.J., Grim, M.E. Belief, Behavior, and Belonging: How Faith is Indispensable in Preventing and Recovering from Substance Abuse. J Relig Health 58, 1713–1750 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10943-019-00876-w
- 11Moreira-Almeida, A., Neto, F. L., & Koenig, H. G. (2006). Religiousness and mental health: a review. Revista brasileira de psiquiatria (Sao Paulo, Brazil : 1999), 28(3), 242–250. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1516-44462006000300018
- 12Umberson, D., & Montez, J. K. (2010). Social relationships and health: a flashpoint for health policy. Journal of health and social behavior, 51 Suppl(Suppl), S54–S66. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022146510383501
- 13Behere, P. B., Das, A., Yadav, R., & Behere, A. P. (2013). Religion and mental health. Indian journal of psychiatry, 55(Suppl 2), S187–S194. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5545.105526 (Retraction published Indian J Psychiatry. 2019 Jan;61(Suppl 3):S632)
- 14Brown, Q. L., Linton, S. L., Harrell, P. T., Mancha, B. E., Alexandre, P. K., Chen, K. F., & Eaton, W. W. (2014). The influence of religious attendance on smoking. Substance use & misuse, 49(11), 1392–1399. https://doi.org/10.3109/10826084.2014.912224










