Hair loss can be a distressing experience for women, impacting their health and self-esteem. While it is normal to lose around 50-100 hairs per day, excessive hair shedding can be a sign of an underlying condition. Understanding the causes of hair loss in women is crucial in finding effective solutions and treatments. This article will explore some common illnesses that can cause hair loss in women and provide insights on how to address this issue.
5 Illnesses that can Cause Hair Loss in Females
- Thyroid Disorders – Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can cause hair loss in women. Thyroid hormones play a vital role in the regulation of hair growth, and an imbalance can result in hair thinning or loss.
- Anaemia – Anaemia is a condition characterised by a deficiency of red blood cells or haemoglobin in the blood. Without enough red blood cells, the hair follicles may not receive adequate oxygen and nutrients, leading to hair loss.
- Lupus – Lupus is an autoimmune disease that can cause inflammation throughout the body, including the scalp. This inflammation can affect hair follicles and result in hair loss.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) – PCOS is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. High levels of androgens (male hormones) in women with PCOS can cause hair thinning or male-pattern hair loss.
- Scalp Infections – There are various scalp infections that can cause hair loss in women such as psoriasis, ringworm and folliculitis to name a few.
1) Thyroid Disorders
 Thyroid disorders are a common cause of hair loss in women. The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, and an imbalance can disrupt the hair growth cycle. There are two types of thyroid disorders that can cause hair loss:
Thyroid disorders are a common cause of hair loss in women. The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, and an imbalance can disrupt the hair growth cycle. There are two types of thyroid disorders that can cause hair loss:
- Hypothyroidism: When the thyroid gland is under-active and does not produce enough hormones, it can lead to hair loss. Other symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, and dry skin.
- Hyperthyroidism: When the thyroid gland is overactive and produces too much hormones, it can also cause hair loss. Other symptoms of hyperthyroidism include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety.
Hair loss caused by thyroid disorders is usually reversible with proper treatment for the underlying condition. If you suspect that your hair loss may be due to a thyroid disorder, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to get accurate diagnosis and treatment.
It is crucial to address the underlying medical condition to prevent further hair loss and promote healthy hair growth. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, eating a balanced diet, and managing stress can also contribute to maintaining healthy hair.
Remember, if you are experiencing excessive hair loss or have concerns about your hair, it is always best to seek advice from a medical professional. They can help determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment options.
2) Anaemia
Anaemia is a condition characterised by a deficiency of red blood cells or haemoglobin in the blood, resulting in reduced oxygen supply to the body’s tissues. While it can affect both men and women, women are particularly susceptible due to reasons such as menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause. One of the lesser-known effects of anaemia is hair loss in women. The link between anaemia and hair loss lies in the fact that hair follicles require an adequate blood supply to grow and maintain healthy hair. When the body lacks sufficient iron and other essential nutrients, hair follicles become weak and can enter a resting phase, leading to hair thinning and eventually hair loss.
To treat hair loss caused by anaemia, it is crucial to address the underlying cause, which in this case is the deficiency of iron or other nutrients. Here are some potential treatment options:
- Iron supplementation: Consuming iron-rich foods such as red meat, poultry, leafy greens, and legumes can help replenish iron levels in the body. In some cases, doctors may also prescribe iron supplements to boost iron stores more quickly.
- Vitamin C intake: Enhancing the absorption of iron can be achieved by pairing iron-rich foods or supplements with foods high in vitamin C. Citrus fruits, berries, and broccoli are excellent sources of vitamin C.
- Balanced diet: Maintaining a well-balanced diet is crucial to ensure the body receives all the necessary nutrients, including iron, vitamin B12, and folate. Leafy greens, eggs, dairy products, nuts, and whole grains should be included in the diet.
- Avoiding caffeine and calcium-rich foods: Both caffeine and calcium can hinder iron absorption. Limiting the consumption of coffee, tea, and excessive dairy products close to meals can optimise the absorption of iron from food sources.
- Medical assessment: If dietary changes and supplements do not show improvement, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation. They may recommend additional tests, such as blood tests or hormonal evaluations, to identify other potential causes of hair loss.
It is worth noting that hair regrowth takes time and patience. With the correct treatment and addressing the underlying anaemia, hair growth can gradually resume. However, it is important to remember that each individual’s response to treatment may vary. Therefore, seeking advice from a healthcare professional is essential to determine the most appropriate and effective course of action.
3) Lupus
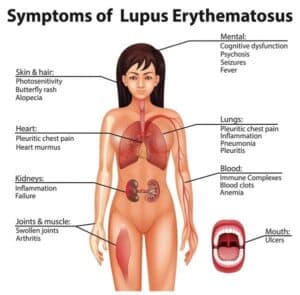 Lupus, a chronic autoimmune disease, has been known to cause hair loss in women. Hair loss, also known as alopecia, can be a distressing symptom for those living with lupus. The exact mechanism behind the connection between lupus and hair loss is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from the inflammatory nature of the disease. The immune system mistakenly targets healthy tissues, including the hair follicles, leading to hair thinning or even complete baldness.
Lupus, a chronic autoimmune disease, has been known to cause hair loss in women. Hair loss, also known as alopecia, can be a distressing symptom for those living with lupus. The exact mechanism behind the connection between lupus and hair loss is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from the inflammatory nature of the disease. The immune system mistakenly targets healthy tissues, including the hair follicles, leading to hair thinning or even complete baldness.
There are different types of lupus-related hair loss. The most common is called diffuse thinning, where hair becomes noticeably thin across the scalp. Another type, known as discoid lupus erythematosus, is characterised by round patches of hair loss that may leave scarring. In some cases, hair loss may also extend beyond the scalp and involve eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair.
When it comes to the treatment of lupus-related hair loss, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional, typically a dermatologist or rheumatologist with expertise in treating lupus. They will assess the severity of hair loss and develop an individualised treatment plan based on the specific needs of the patient.
Treatment options can vary, and it often involves a combination of approaches. Here are some common methods used:
- Medications: Corticosteroids, such as topical creams or injections, may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system’s abnormal response. Other medications, like hydroxychloroquine, can also be beneficial in managing lupus symptoms.
- Topical treatments: Minoxidil, an over-the-counter topical solution, can help stimulate hair growth and improve overall hair density. It is typically applied directly to the scalp.
- Light therapy: In cases of discoid lupus, phototherapy may be recommended. This treatment involves exposing the affected areas to targeted ultraviolet (UV) light to help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
- Wigs or hairpieces: Some women may opt for wigs, hair extensions, or hairpieces to improve their appearance while waiting for hair regrowth.
- Camouflage techniques: Various cosmetic products, such as powders, sprays, or hair fillers, can help conceal areas of hair loss and give the illusion of fuller hair.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of these treatments may vary from person to person. It may take time to see noticeable improvements, and a trial-and-error approach may be required to find the most suitable treatment regimen.
Moreover, managing stress, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and following a well-balanced diet can also contribute to overall well-being and may indirectly benefit hair health. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals will ensure the treatment plan is adjusted as needed and any concerns or questions are addressed.
4) Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
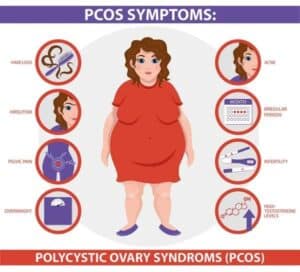 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects many women during their reproductive years. One of the common symptoms associated with PCOS is hair loss. This condition, called female pattern hair loss occurs due to hormonal imbalances and increased sensitivity of hair follicles to androgen hormones.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects many women during their reproductive years. One of the common symptoms associated with PCOS is hair loss. This condition, called female pattern hair loss occurs due to hormonal imbalances and increased sensitivity of hair follicles to androgen hormones.
The cause of hair loss in women with PCOS is primarily linked to elevated levels of androgens, such as testosterone, in their bodies. These androgens can suppress hair follicle growth and shorten the hair’s growth cycle, leading to thinning and shedding of hair. In addition, the excess androgens in PCOS can also increase the production of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone known to contribute significantly to hair loss.
Fortunately, there are several treatment options available for women experiencing hair loss due to PCOS. These treatments aim to address the underlying hormonal imbalances and reduce the effects of androgens on the hair follicles.
- Medications: Your doctor may prescribe medications such as oral contraceptives (birth control pills) or anti-androgens to regulate hormone levels and reduce the effects of androgens on the hair follicles. These medications can help slow down hair loss and promote hair regrowth.
- Topical treatments: Minoxidil, a topical medication, is commonly used to stimulate hair growth. Applied directly to the scalp, minoxidil can help increase blood flow to the hair follicles and extend the duration of the hair’s growth phase. Regular use of minoxidil can lead to fuller and thicker hair.
- Lifestyle changes: Making certain lifestyle modifications can also be beneficial in managing PCOS-related hair loss. Maintaining a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise can help regulate hormone levels and promote overall well-being. Additionally, reducing stress levels and practicing relaxation techniques may alleviate the impact of stress-induced hair loss.
- Hair restoration procedures: In some cases, women with PCOS may opt for hair restoration procedures such as hair transplantation or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy. These procedures can stimulate hair growth in areas where thinning or balding has occurred.
It’s important to remember that treating hair loss associated with PCOS may require a comprehensive approach, including both medical interventions and lifestyle adjustments. Consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist or endocrinologist, is crucial to determine the most suitable treatment options based on individual circumstances.
5) Scalp Infections
Scalp infections can wreak havoc on a woman’s hair, leading to hair loss and other related issues. It is essential to understand the common scalp infections and their effects on hair growth to address the problem effectively.
Fungal Infections
Fungal infections, such as ringworm (tinea capitis), can cause hair loss and scalp itching. These infections are highly contagious and can spread from person to person through direct contact. Fungal infections can disrupt the hair growth cycle, leading to thinning hair and bald patches.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections like folliculitis and cellulitis can also affect hair growth. Folliculitis occurs when hair follicles become infected, leading to redness, inflammation, and pustules. Cellulitis is a more severe bacterial infection that can spread to the deeper layers of the skin. Both conditions can cause hair loss in affected areas.
Viral Infections
Viral infections, such as shingles (herpes zoster) and scalp herpes (herpes simplex), can also contribute to hair loss. These infections can cause inflammation and damage the hair follicles, leading to hair thinning and breakage.
Treating Scalp Infections
If you suspect a scalp infection as the cause of your hair loss, it is crucial to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. Your doctor may prescribe anti-fungal, antibacterial, or antiviral medications depending on the specific infection. Additionally, following these guidelines can help manage and prevent scalp infections:
- Maintain good hygiene: Regularly wash your hair and scalp to keep them clean and free from bacteria and fungi.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Do not share combs, brushes, hats, or towels with others, as this can increase the risk of spreading or contracting infections.
- Protect your scalp: If you participate in activities where your scalp may come into contact with potentially infected surfaces, such as wrestling or swimming, take precautions such as wearing protective gear or using a swimming cap.
- Avoid scratching: Refrain from scratching your scalp as it can worsen the infection and damage the hair follicles.
- Boost your immune system: A strong immune system can help prevent and fight off infections. Maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough rest.
Understanding the different scalp infections and their effects on hair growth is crucial in finding the right treatment and preventing further hair loss. If you suspect a scalp infection, consult with a healthcare professional to receive proper guidance and care.








